Controls
Controls are predefined countermeasures that can be used to systematically address attack scenarios. They represent reusable security measures that are automatically generated to mitigate configurable attack vectors and threat rules, providing a consistent and efficient approach to threat mitigation.
Controls can be:
- Linked to attack vectors and threat rules for automatic countermeasure generation
- Associated with MITRE EMB3D framework entries for standardized security practices
- Connected to checklist requirements for compliance tracking
- Documented with implementation guidance to help development teams
Basic Settings
Each control includes the following basic configuration options:
- Name: A unique identifier for the control (e.g., "Input Validation", "Encryption at Rest")
- Description: A detailed explanation of what the control does and how it mitigates threats
- Mitigated Attack Vectors: List of attack vectors mitigated by this control (used for countermeasure generation)
- Mitigated Threat Rules: List of threat rules mitigated by this control (used for countermeasure generation)
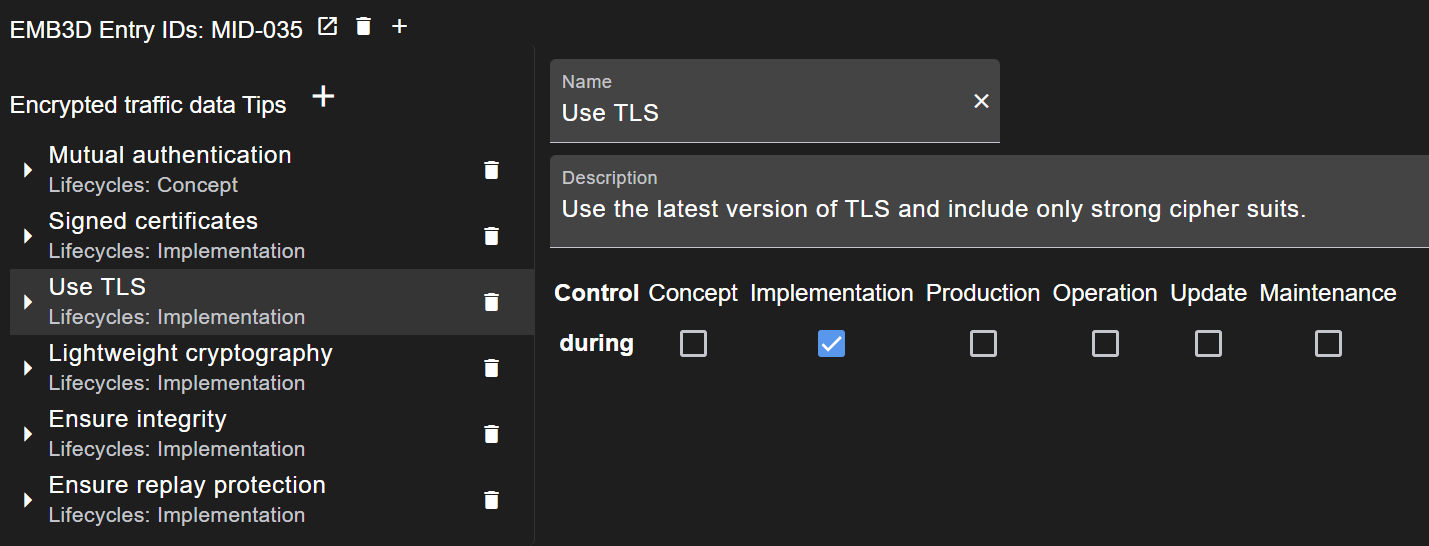
MITRE EMB3D Integration
Controls can be linked to MITRE EMB3D™ entries to align your countermeasures with industry-standard security practices.
To link a control to MITRE EMB3D:
- Select the control in the configuration
- Click on the add button
 next to EMB3D Entry IDs
next to EMB3D Entry IDs - Add the ID, e.g.
12
Implementation Tips
Each control can include implementation guidance to help developers and security teams properly implement the countermeasure. Implementation tips should include:
- Technical guidance: Specific technologies, libraries, or approaches to use
- Best practices: Recommended patterns and anti-patterns
- Configuration examples: Sample code or configuration snippets
- Verification methods: How to verify the control is properly implemented
- Common pitfalls: Known issues to avoid during implementation
Automatic Countermeasure Generation
When threat rules are evaluated during threat generation, controls associated with matching rules are used to generate countermeasures. This process:
- Identifies applicable controls based on elements, attack vectors, and threat rules
- Generates countermeasures in the threat model
- Applies control description
Checklist Requirements Linking
Controls can be directly linked to specific checklist requirements, enabling automatic traceability between requirements and countermeasures.
When a control is implemented, all linked checklist requirements can be automatically updated, streamlining the compliance verification process.
Best Practices
When configuring controls in TTModeler, consider the following best practices:
- Reusability: Define controls at the appropriate abstraction level to maximize reuse across different threat rules
- Specificity: Provide sufficient detail in descriptions and implementation tips to be actionable
- Traceability: Link controls to relevant MITRE EMB3D entries and checklist requirements to maintain traceability
- Maintenance: Regularly review and update controls as security standards and best practices evolve
- Consistency: Use consistent naming conventions and categorization for easier navigation