Checklist
Using a Checklist
This section describes how checklists can be used to track the fulfillment of a requirement list such as IEC 62443-4-2. Checklists can be added to a device in the project tree.
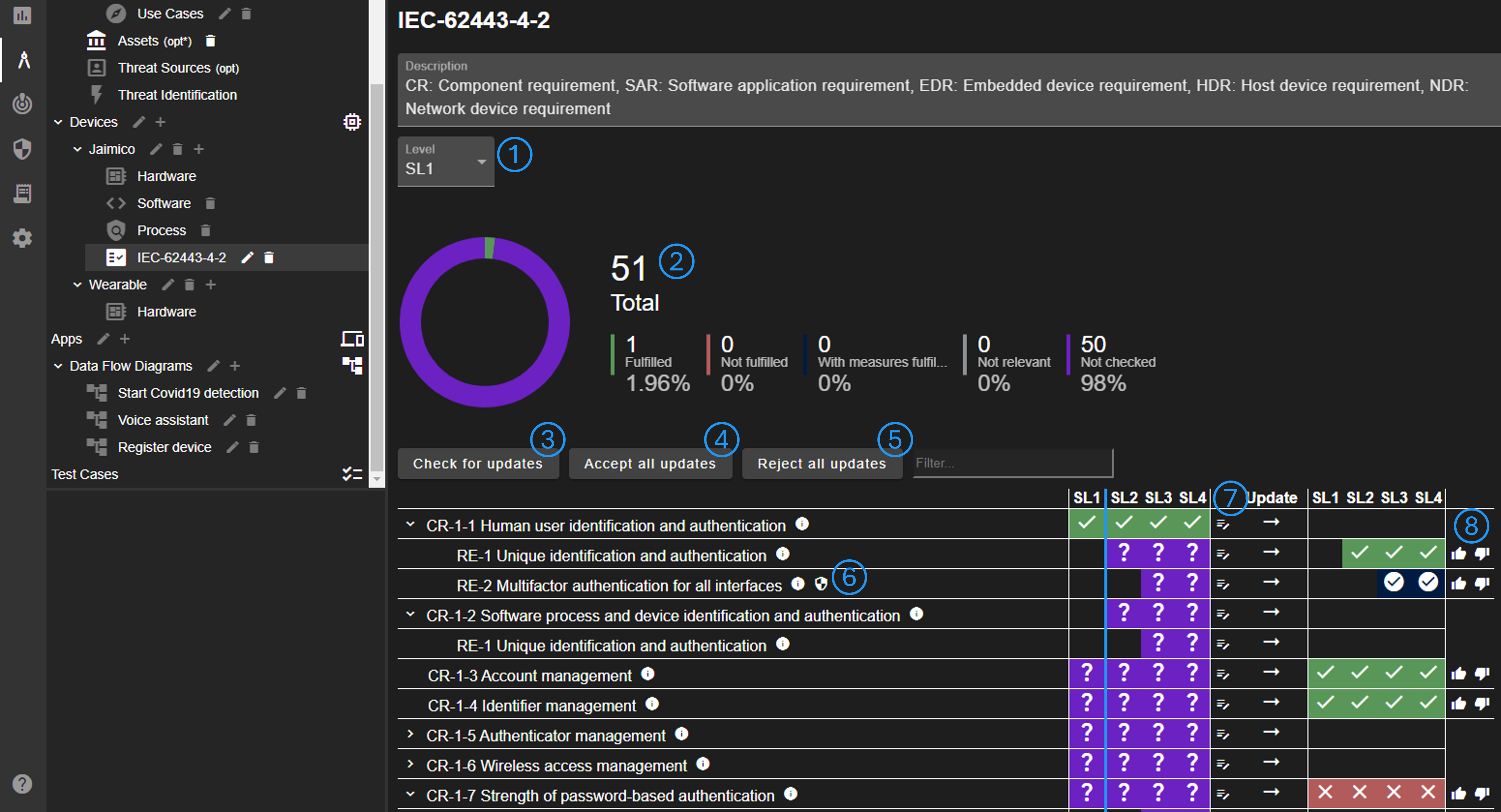
It is possible to change the target level (No. 1). The chart showing the fulfillment statistics updates accordingly (No. 2).
There may be pre-configured detection rules. The device can be checked against the detection rules (No. 3) and updates may be suggested. It is possible to accept all updates (No. 4), reject all updates (No. 5), or decide individually (No. 8).
All requirements are listed below the chart. Requirement description, explanation, linked countermeasures, and the detection rule can be view (No. 6). The state of a requirement (e.g. fulfilled or not fulfilled) can be changed by clicking on the colored boxes. Futhermore, notes for each requirement can be entered (No. 7).
Configuration
This section describes the configuration of checklists and how to change a checklist or define a completely new one.
To configure a checklist, go to configuration via the side navigation bar and then open the tab 'Checklists'.
General Settings
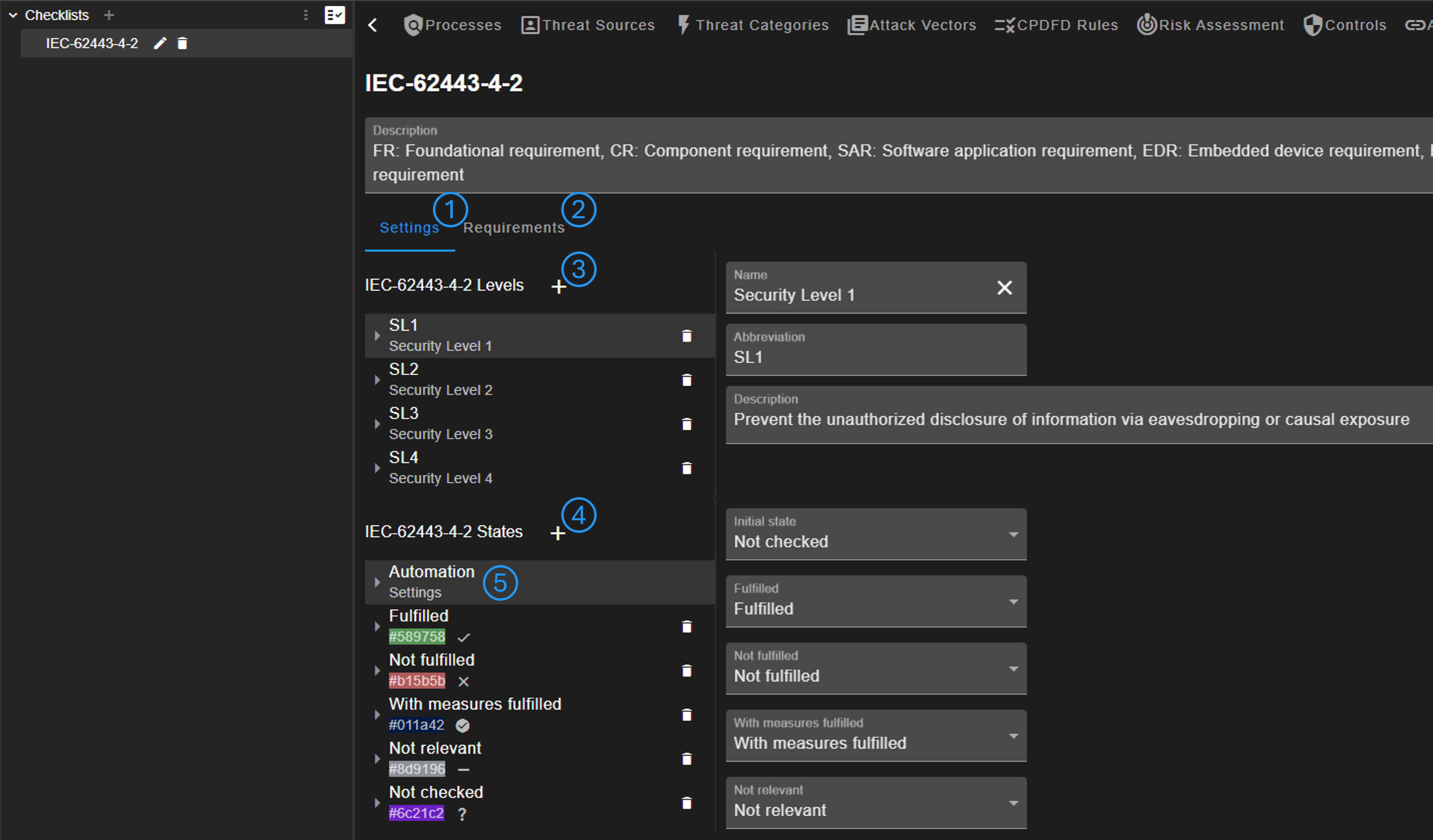
A checklist contains general settings (No. 1) and the list of requirements (No. 2). Is is possible to define multiple levels for a checklist (No. 3). Note that at least one level is required, even if a checklist does not define different levels. The states of a checklist can also be configured (No. 4). Settings for the states can be changed (No. 5). These state settings are used for the initial state and automations.
Requirements Configuration
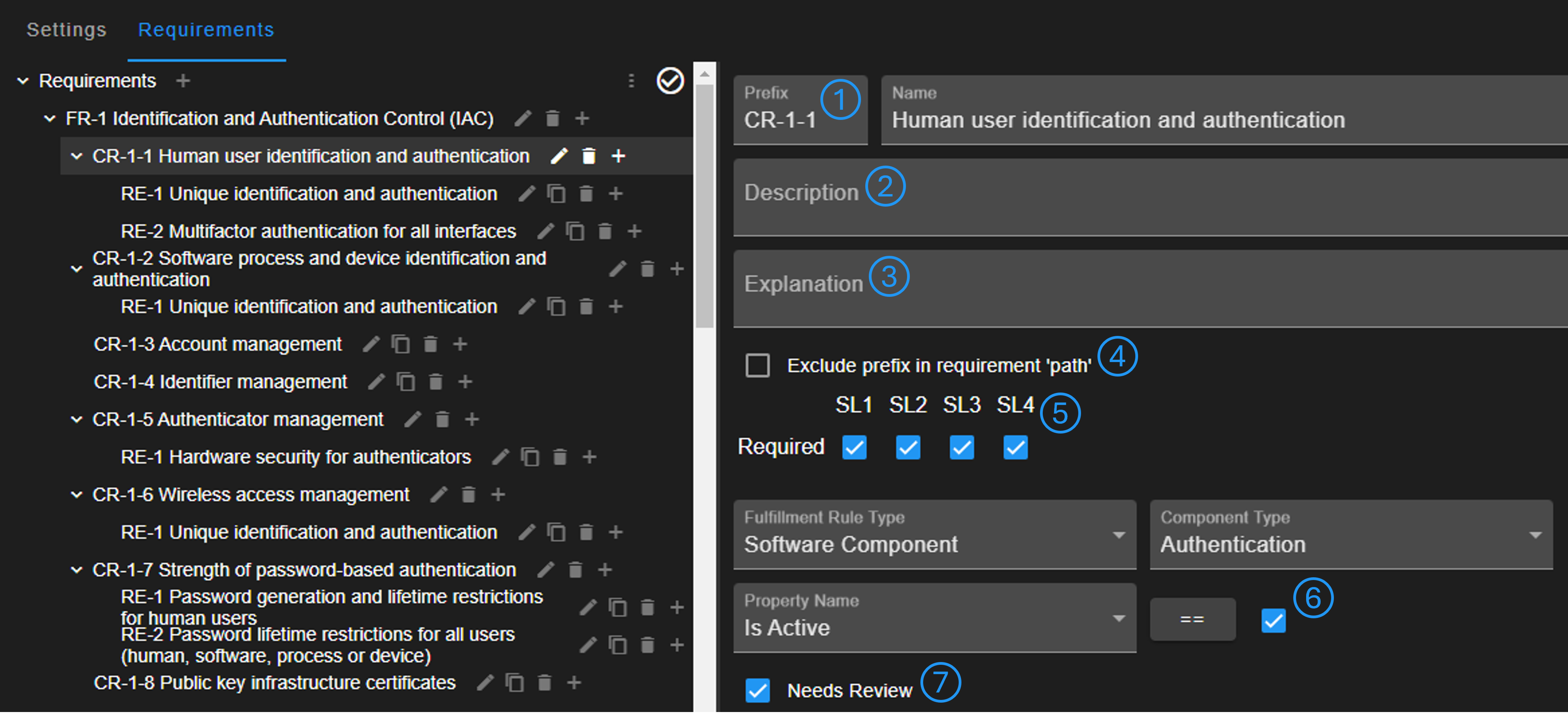
Requirements can be hierarchically configured in the inner navigation tree shown on the left side of the image. Requirements should include a prefix (No. 1), the description according to the checklist (No. 2), and an optional explanation for further guidance (No. 3).
When requirements are referenced in the project report, the full prefix-path of the navigation tree is shown to assure correct identification. If the prefix should not be shown in this prefix-path, it can be excluded (No. 4).
It must be configured for each level whether a requirement is required to fulfill the checklist (No. 5).
A detection rule for automatically setting whether a requirement is fulfilled or not can be defined (No. 6). It is possible to use the boolean properties of software components to decide whether the requirement is fulfilled. It can be defined whether users must review and manually accept the detection (No. 7).